FA/MV LENS TECHNOLOGY
Various types of lenses are used in machine vision systems. In
order to achieve the highest performance, it is important to select
the lens most suitable for the application.

Quick selection – How to calculate focal length
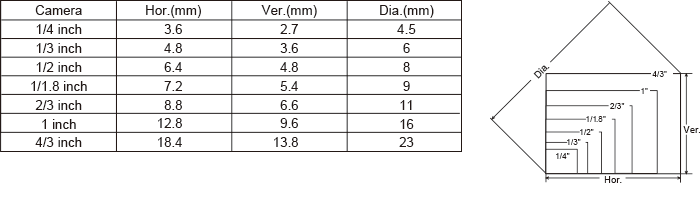
Ex) A 2/3″ camera is used to capture an object 100mm wide from a distance of 300mm.
Use the picture below and the image size chart to substitute for Y, L, and Y’. Then, to capture the entire object, use the formula f=L*Y’/Y to calculate focal length.
Y’=8.8mm(See image size chart), L=300mm, Y= 100mm
f = 300*8.8/100
f=26.4mm.
The most appropriate lens is f=25mm lens, which is close but not greater than the 26.4 derived from the calculation.
Lenses with shorter focal lengths than the given number can capture an object in its entirety.
Quick selection – How to calculate the angle of view
Ex ) A 1/2″ camera is used to shoot an object 300mm away. The focal length of the lens is16mm. Use the picture below and image size chart to substitute for f, L, and Y1 (H or V accordingly). Then to calculate the angle of view, use the formula Y= L*Y’/f.
Width- Y’=6.4mm (Horizontal), f= 16mm, L=300mm
Y= 300*6.4/ 16
Y= 120mm
Vertical-Y’ =4.8mm (Vertical), f= 16mm, L=300mm
Y=300*4.8/16
Y=90mm
Thus in order to capture the object in its entirety, the maximum dimensions of an object at a distance of 300mm is 120mm wide and 90mm height.
Characteristics of lenses are descrubed below
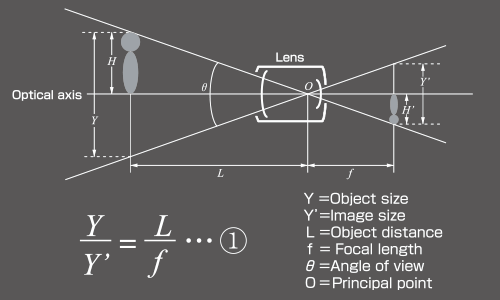
Object size · · · · · Field range which can be captured by the image sensor
Image size · · · · · See description
Object distance · ·Distance from the lens to the object
Focal length · · · · Distance from the pricipal point to the focus point
Angle of view
· · · ·This angle represents a shooting range in degrees.The
shorter a focal length is, the bigger an angle of view is.
Principal point · · · Optical center of the lens
Image Size
Image size represents size of camera sensor
F-number
The F-number represents the amount of light that passes through a lens. As the F-number decreases, the amount of light that passes through the lens increases. The F-number affects the depth of field as mentioned below.
Depth of field
Depth of field is the range of distane, in front of and behind a subject that appears infocus. If the depth of field is deep, an object will appear to be in focus even if it moves slightly back and forth.
The characteristics of depth of field (comparing lenses with the same specifications)
- · Increasing the F-number (darker) increases the depth.
- · Shortening the focal length increases the depth.
- · Lengthening the object distance increases the depth.
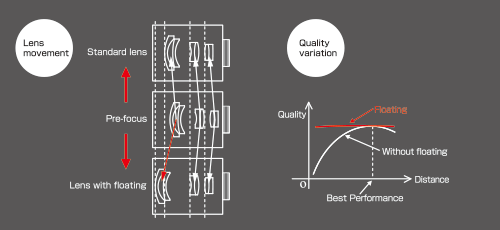
Floating mechanism system
The floating mechanism system is effective in preventing malfunction and increasing the life of the lens. It is also called the close distance aberration compensation mechanism.
In standard CCTV lenses, the whole or a part of the lens moves when focusing. However, moving one lens element and not the entire lens system changes the direction of the light rays and decreases the optical performance.
However, lenses with the floating mechanism system can vary the distance between the lens elements. This enables the lens to achieve the highest performance at various objective distances.