Basic functions of lenses
Lenses are used as part of a camera system to accurately capture images of objects; in the factory automation field, they are used in applications as diverse as part inspection, product positioning, and robot vision systems. Since high-precision image acquisition is required, it is essential to select the appropriate lens.
Lens type
The main types of lenses used in the FA field are as follows:
Fixed focal length lens

A fixed-focus lens features its focal length fixed and has no focusing mechanism. Also called a single focal length lens, it has less distortion and aberration than zoom lenses, and its simple structure provides high resolution and good image quality. Fixed-focus lenses are optimized for specific field-of-view angles and shooting distances, making them easy to install and relatively inexpensive.
Telecentric lenses

Telecentric lenses are used to image objects the same size as the image sensor in the camera. These lenses are not affected by incident light from the surroundings because they are designed to image only collimated light from the object. Therefore, both distant and nearby objects of the same size can be imaged in the same size and in focus. It is suitable for dimensional measurement and high-precision inspection, enabling accurate evaluation of products.
Macro Lens/Macro Zoom Lens
Macro lenses are designed for close-up distance imaging. These lenses are suitable for making objects (subjects) appear larger and for inspecting minute parts and details. In particular, macro zoom lenses feature continuously variable magnification and a constant (unchanging) focal length. This makes it possible to acquire detailed images flexibly.
Line scan lens

Designed for line-scan cameras, these lenses are used to acquire continuous line images. Suitable for inspection and quality control in high-speed production lines, they are effective for detecting product defects and measuring dimensions. Line scan lenses are essential for capturing moving objects with high accuracy.
Varifocal lenses

Varifocal lenses can change the focal length as desired. It can zoom in and out – also called variable focal length lenses. Changing the shooting range causes the lens to lose focus, requiring manual re-focusing. The advantage is that it can be adjusted after installation and is less expensive than zoom lenses. The optimum shooting range is set at the time of installation and can be adjusted flexibly afterward.
Zoom lens
A zoom lens can continuously change the angle of view. Unlike varifocal lenses, the focus position does not change when the angle of view is changed. Therefore, it is possible to continuously change the angle of view and optical magnification after installation. However, if the flange back of the camera is out of alignment, the focus will shift when zooming, so the flange back adjustment mechanism is required on either the lens or the camera when using the lens. Zoom lenses are suitable for situations that require flexible imaging.
Tips for choosing lenses
When choosing a lens, it is important to consider the following points:
Image size
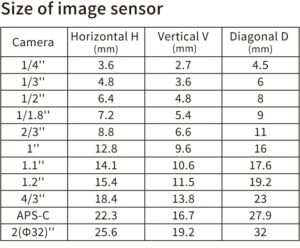
Image size indicates the area that can be seen through the lens. Lenses can be used as long as they have image size greater than or equal to the camera’s sensor size. By selecting the appropriate image size, the entire object to be captured can be accurately imaged.
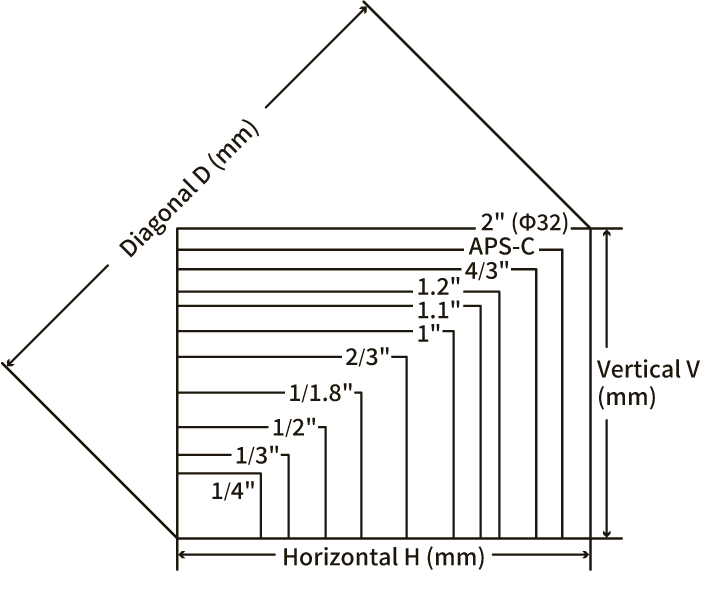
Focal length
The shooting range is determined by the focal length, sensor size, and the distance from the lens to the subject (WD). Focal length is the distance from the lens to the image sensor. When the focal length is long, the subject can be magnified. When capturing the subject, you can choose a lens with a different focal length to match the size and WD of the subject you are imaging.
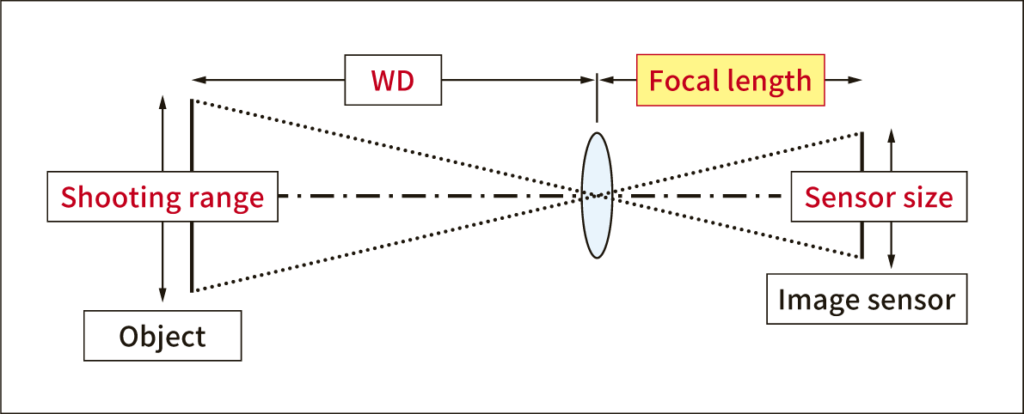
F-stop (aperture)
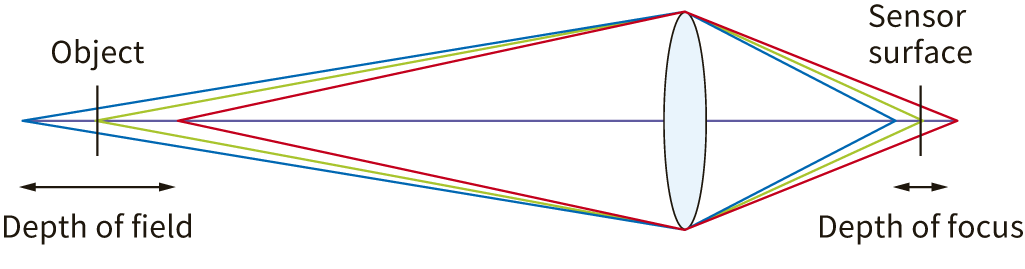
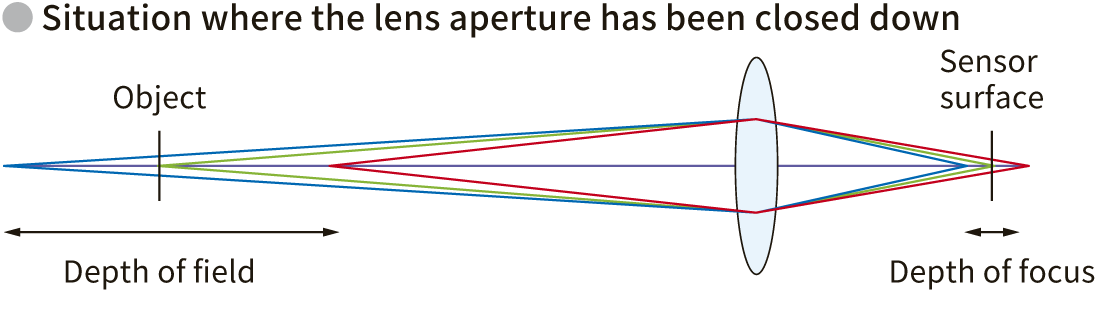
The brightness of a lens is expressed as the focal length divided by the effective diameter of the lens. The f-number can be adjusted with the f-stop aperture; the smaller (brighter) the f-stop, the faster the shutter speed; the larger (darker) the f-stop, the wider the range in which the subject is in focus (depth of field).

Depth of field
Depth of field is the area in focus. Depth of field is determined by f-stop, WD, and focal length; increasing f-stop, shortening focal length, and lengthening WD will increase depth of field. By adjusting the depth of field, you can capture the entire object being captured in sharp detail.
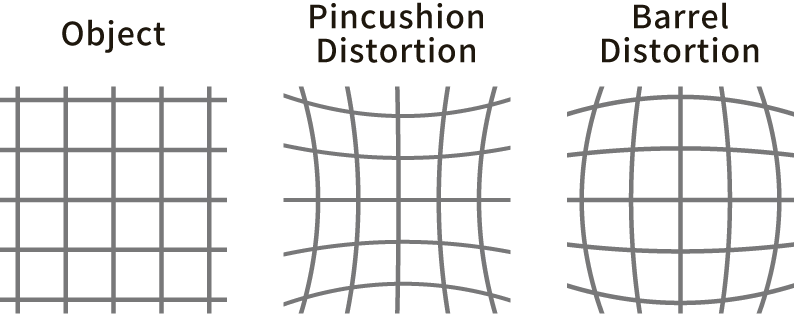
Distortion
Distortion is the phenomenon of image deformation. If the captured image is distorted, the captured subject will appear different from its actual shape. In other words, it causes errors in the positional information of the subject during inspection and image processing. Therefore, low distortion lenses can be considered high performance.
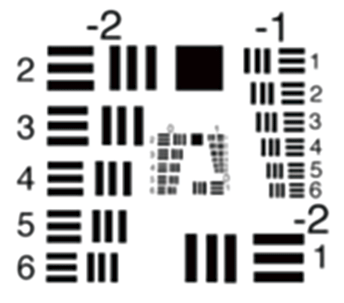
Resolution
Resolution is the degree to which object outlines and details can be expressed in fine detail. Resolution can be expressed in terms of the number of discernible black and white stripes drawn within a width of 1mm. Stripe pattern is described by the fineness of stripes and is expressed in lp (line pairs)/mm.
Floating
Floating mechanism is effective mechanism to minimize performance degradation. It is also called the close-range aberration correction mechanism. In normal lenses, the entire lens is moved when focusing. As a result, performance changes depending on the WD. Lenses equipped with a floating mechanism have multiple internal lens groups that move independently to prevent performance degradation due to WD. Thus, the lens is able to perform at near maximum performance in all WDs.


Lens maintenance
Not only choosing the right lens, but also maintaining the lens is important. Regular cleaning and inspection will help maintain lens performance and ensure high quality images over the long term. Failure to maintain the lens may result in poor lens performance and image quality. When cleaning and inspecting, it is important to use special cleaning products carefully.
Summary
Choosing lenses in the field of FA requires consideration of various factors such as image size, focal length, “f-stop” (aperture), depth of field, distortion, resolution, and floating. Choosing the appropriate lens can increase the efficiency of the manufacturing process and improve quality. It is important to select the most appropriate lens for the specific application and environment, then perform regular maintenance.
Professional knowledge and experience are required in lens selection. If necessary, expert advice will help you select the most appropriate lens. Understanding how to select lenses in the FA field and making the appropriate choice will greatly improve the efficiency and quality of your production site.
If you need help choosing lenses, please contact us using the form below.
We offer a wide range of over 140 types of lenses and will recommend the most suitable one for you.


